Which Of The Following Is Defined As Combinations Of Soil Particles That Vary In Size And Shape?
What is Particulate Matter?
Airborne particulate thing (PM) is not a single pollutant, but rather is a mixture of many chemic species. It is a complex mixture of solids and aerosols composed of small droplets of liquid, dry out solid fragments, and solid cores with liquid coatings. Particles vary widely in size, shape and chemical composition, and may contain inorganic ions, metallic compounds, elemental carbon, organic compounds, and compounds from the earth's crust. Particles are divers by their bore for air quality regulatory purposes. Those with a diameter of 10 microns or less (PM10) are inhalable into the lungs and tin induce agin wellness effects. Fine particulate matter is divers every bit particles that are 2.5 microns or less in diameter (PM2.5). Therefore, PM2.5 comprises a portion of PM10.
What is the Difference Betwixt PM10 and PM2.five?
PM10 and PM2.5 often derive from dissimilar emissions sources, and also have dissimilar chemic compositions. Emissions from combustion of gasoline, oil, diesel or wood produce much of the PM2.5 pollution found in outdoor air, as well every bit a pregnant proportion of PM10. PM10 also includes grit from construction sites, landfills and agriculture, wildfires and brush/waste burning, industrial sources, current of air-diddled grit from open lands, pollen and fragments of bacteria.
PM may be either directly emitted from sources (primary particles) or formed in the atmosphere through chemical reactions of gases (secondary particles) such as sulfur dioxide (Then2), nitrogen oxides (NOX), and certain organic compounds. These organic compounds can be emitted by both natural sources, such equally copse and vegetation, every bit well as from human being-fabricated (anthropogenic) sources, such every bit industrial processes and motor vehicle exhaust. The relative sizes of PM10 and PM2.five particles are compared in the figure beneath.
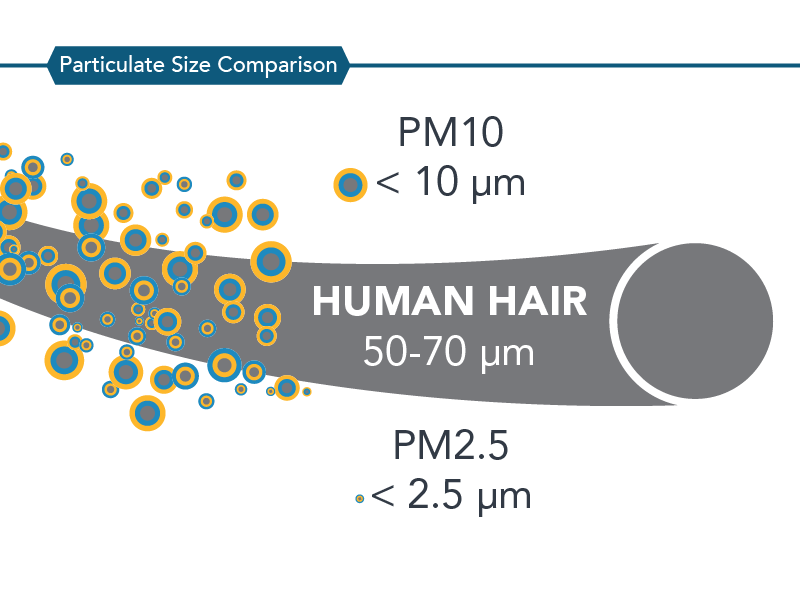
Why is CARB Concerned about PM10 and PM2.five?
CARB is concerned about air-borne particles because of their effects on the health of Californians and the surroundings. Both PM2.5 and PM10 tin be inhaled, with some depositing throughout the airways, though the locations of particle deposition in the lung depend on particle size. PM2.5 is more likely to travel into and deposit on the surface of the deeper parts of the lung, while PM10 is more likely to eolith on the surfaces of the larger airways of the upper region of the lung. Particles deposited on the lung surface can induce tissue damage, and lung inflammation.
What Kinds of Harmful Effects Can Particulate Thing Cause?
A number of adverse health impacts take been associated with exposure to both PM2.5 and PM10. For PM2.5, short-term exposures (up to 24-hours duration) have been associated with premature mortality, increased infirmary admissions for heart or lung causes, acute and chronic bronchitis, asthma attacks, emergency room visits, respiratory symptoms, and restricted activity days. These adverse health effects accept been reported primarily in infants, children, and older adults with preexisting center or lung diseases. In add-on, of all of the common air pollutants, PM2.5 is associated with the greatest proportion of adverse health effects related to air pollution, both in the U.s. and world-wide based on the Earth Health Organisation'southward Global Burden of Illness Project.
Curt-term exposures to PM10 have been associated primarily with worsening of respiratory diseases, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), leading to hospitalization and emergency department visits.
Long-term (months to years) exposure to PM2.5 has been linked to premature death, peculiarly in people who have chronic heart or lung diseases, and reduced lung office growth in children. The effects of long-term exposure to PM10 are less clear, although several studies propose a link between long-term PM10 exposure and respiratory mortality. The International Bureau for Research on Cancer (IARC) published a review in 2015 that concluded that particulate matter in outdoor air pollution causes lung cancer.
Diesel fuel PM: A special grade of particulates. The solid material in diesel fuel exhaust is known as diesel particulate matter (DPM). More than 90% of DPM is less than 1 µm in diameter (about 1/70th the diameter of a man hair), and thus is a subset of PM2.5. More than Information
Who is at the Greatest Chance from Exposure to Particulate Thing?
Research points to older adults with chronic heart or lung disease, children and asthmatics as the groups near likely to experience adverse wellness effects with exposure to PM10 and PM2.5. Also, children and infants are susceptible to harm from inhaling pollutants such equally PM because they inhale more air per pound of body weight than practise adults - they exhale faster, spend more time outdoors and have smaller body sizes. In addition, children'due south young immune systems may crusade them to be more susceptible to PM than salubrious adults.
Research from the CARB-initiated Children's Health Study found that children living in communities with high levels of PM2.v had slower lung growth, and had smaller lungs at age 18 compared to children who lived in communities with depression PM2.5 levels.
CARB used the U.Southward. EPA'south risk cess methodology to conduct an assessment of premature mortality associated with exposure to PM2.5 (California Air Resource Board 2010). An update to this assay using ambient air quality data from 2014-2016 indicated that PM2.five exposure contributes to 5,400 (uncertainty range of 4,200 – half-dozen,700) premature deaths due to cardiopulmonary causes per year in California. In addition, PM2.5 contributes to about ii,800 hospitalizations for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases (uncertainty range 350 – v,100), and nearly half-dozen,700 emergency room visits for asthma (uncertainty range four,200 – 9,300) each yr in California.
How Does Particulate Matter Affect the Environment?
Particulate affair has been shown in many scientific studies to reduce visibility, and also to adversely affect climate, ecosystems and materials. PM, primarily PM2.5, affects visibility past altering the style lite is captivated and scattered in the atmosphere. With reference to climatic change, some constituents of the ambient PM mixture promote climate warming (e.thou., black carbon), while others have a cooling influence (e.grand., nitrate and sulfate), then ambience PM has both climate warming and cooling backdrop. PM tin adversely touch ecosystems, including plants, soil and water through deposition of PM and its subsequent uptake by plants or its deposition into water where it tin can touch on h2o quality and clarity. The metal and organic compounds in PM have the greatest potential to modify plant growth and yield. PM deposition on surfaces leads to soiling of materials.
Is Particulate Affair a Problem Indoors?
Some of the particulate thing found indoors originates from the outdoors, particularly PM2.5. These particles enter indoor spaces through doors, windows, and "leakiness" in edifice structures. Particles can too originate from indoor sources. Particles of indoor origin include components derived from biological sources, many of which are known allergens, such as pollens, mold spores, dust mites and cockroaches. Indoor activities generate particles, as well, including smoking tobacco, cooking and burning wood, candles or incense. Particles also can form indoors from complex reactions of gaseous pollutants emitted from such sources as household cleaning products and air fresheners.
What are the Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Affair?
Ambient air quality standards define the maximum amount of pollutant that tin can be present in outdoor air without harming homo health. In 2002, afterward an extensive review of the scientific literature, the Lath adopted a new almanac average standard for PM2.5 ppm, and retained the existing annual and 24-hour standard average standards for PM10. The national annual boilerplate PM2.v standard was well-nigh recently revised in 2012 following an exhaustive review of new literature pointed to evidence for increased risk of premature mortality at lower PM2.five concentrations than the existing standard. The 2012 review resulted in retention of the existing 24-hour boilerplate PM2.five and PM10 standards.
| PM2.v | PM10 | |||
| Annual Average | 24-Hour Average | Annual Boilerplate | 24-Hour Average | |
| National Ambience Air Quality Standard | 12 µg/m3 | 35 µg/mthree | None | 150 µg/miii |
| California Ambient Air Quality Standard | 12 µg/m3 | None | 20 µg/k3 | 50 µg/thou3 |
Which Of The Following Is Defined As Combinations Of Soil Particles That Vary In Size And Shape?,
Source: https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/resources/inhalable-particulate-matter-and-health
Posted by: arciniegaseents.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Is Defined As Combinations Of Soil Particles That Vary In Size And Shape?"
Post a Comment